Definition of the skill
Flexibility is the ability to adapt to new situations and changes. It is the willingness to change. It involves being open to different ideas, adjusting to unexpected events, and finding new ways to solve problems. Flexibility is important because life is constantly changing, and being flexible allows us to cope with challenges in a calm and effective way. It’s not just about accepting change, but also being able to adjust our thoughts, emotions, and actions to meet new demands or circumstances, whether they are in our personal life, work or social environment. Flexibility helps us move forward and make the best of difficult situations. There are three skills that are very close in meaning. Sometimes they are used interchangeably, but the difference between them should be clear. These three skills are: flexibility, adaptability, and flexibility
Resiliency is the capacity to recover quickly from difficulties.
Flexibility is willingness to change, ability to easily modify thinking and behavioral strategies while keeping core values in mind.
Adaptability is being able to adjust our thinking and behavior to new conditions.
Complexity of the skill
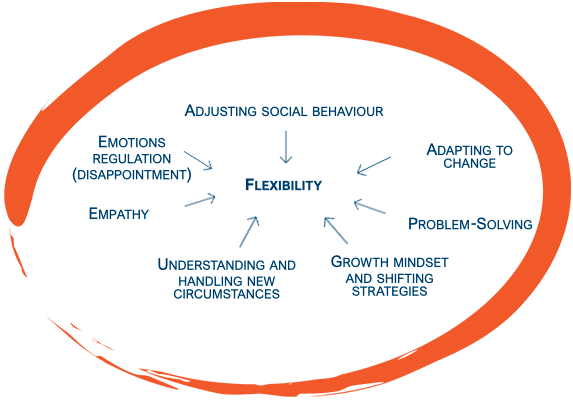
Adapting to change: children are able to quickly adjust to new situations, like a new teacher, a change in class activities, or a different daily routine.
Shifting strategies and handling new circumstances: when faced with difficulties, such as struggling with a task, children show flexibility by trying different approaches to solve problems, rather than giving up. The flexible children are able to adapt to unfamiliar situations, such as going to a new place or meeting new people, without becoming overly anxious or upset.
Growth mindset and creative thinking: Flexible children are able to think in a divergent way, seeking many different, novel/unusual solutions to a situation rather than thinking in terms of one ‘good’ answer. In other words, they use their fantasy to discover new and unexpected connections and apply unconventional approaches.
Adjusting social behaviour: children can adapt their behaviour to suit different social situations, understanding how to interact with peers or adults based on context and social norms.
Managing emotions: if things don’t go as expected, children show flexibility by coping with the situation, adjusting their expectations, and continuing to engage with the task or situation.
